With the development of modern society, the network has become an indispensable part of people’s lives, and the transmission of network signals cannot be separated from network cables (referred to as network cables). Ship and sea work is a modern industrial complex that moves on the sea, with increasing automation and intelligence, and more complex usage environments. The requirements for network cables are naturally higher than those for land environments. Today, I will briefly introduce ship and sea network cables to everyone.
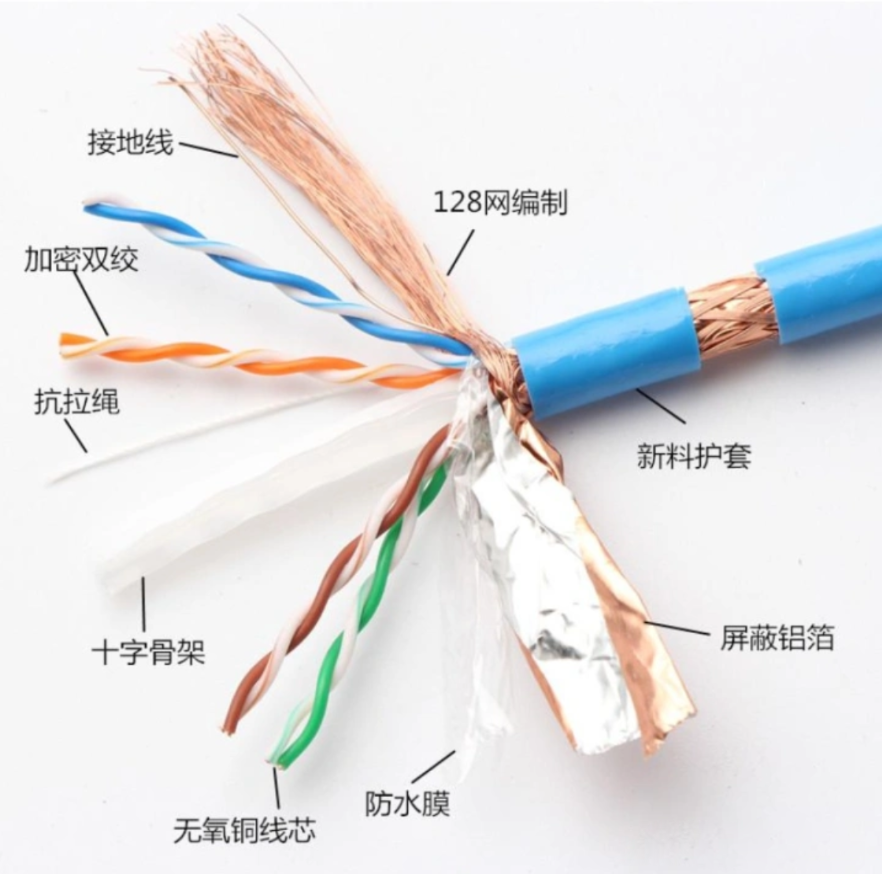
The network cable we are talking about is usually twisted pair. The conductor material of the network cable is copper, with multiple stranded conductors and single stranded solid conductors. Copper conductors with PE or PO insulation are added, twisted counterclockwise in pairs, and then twisted into a cable by four pairs of wires. The cross skeleton, shielding layer, drain wire, and weaving layer are added as needed, and finally the protective sleeve is extruded to complete production.
1.Network cable classification
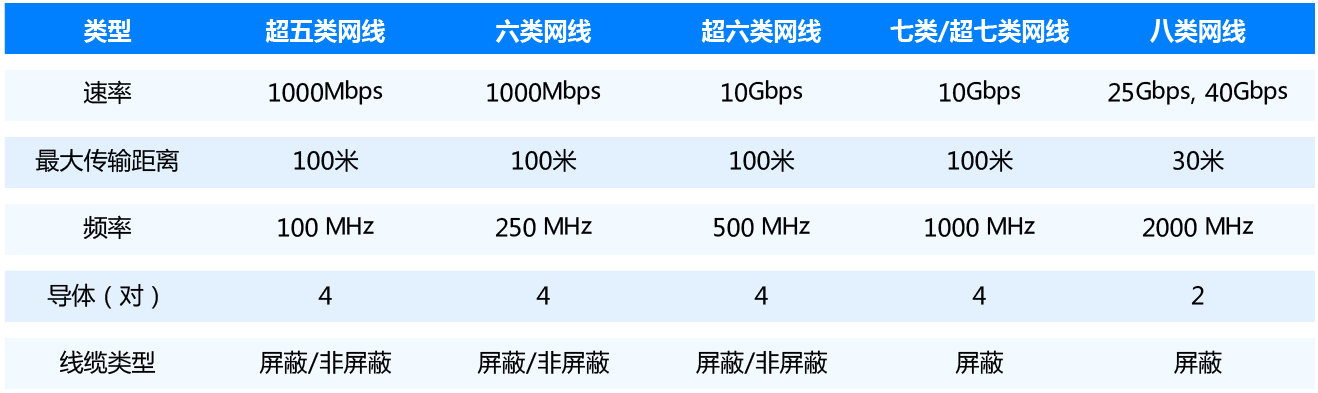
The commonly used network cables can be divided into CAT5E (super five categories), CAT6 (six categories), CAT6A (super six categories), CAT7 (seven categories), CAT7A (super seven categories), CAT8 (eight categories), among which:
Super Class 5 network cable: The outer side of the network cable is marked with CAT.5e, with a transmission frequency of 100MHz and a maximum transmission rate of 1000Mbps, suitable for gigabit networks. Having better performance than Class 5 lines, improving indicators such as NEXT, PS-ELFEXT, Atten, and supporting duplex applications; At present, a large portion of the network cables are classified as Category 5, especially for our own use.
Six types of network cables: The outer side of the network cable is marked with CAT. 6, with a maximum transmission frequency of 250MHz and a maximum transmission rate of 1Gbps, suitable for gigabit networks. The comprehensive attenuation to crosstalk ratio (PS-ACR) of Category 6 cabling systems should have a significant margin at 200MHz, providing twice the bandwidth of Category 5. The transmission performance of Category 6 cabling is much higher than that of Category 5 standards, making it the most suitable for applications with transmission rates higher than 1Gbps.
Super Category 6 network cable: The outer side of the network cable is marked with CAT.6e or CAT6A, with a maximum transmission frequency of 500MHz and a transmission speed of 10Gbps, suitable for use in 10 Gigabit networks. This makes Super Category 6 network cables the most popular twisted pair in cabling systems, and the high performance of Super Category 6 twisted pair cables greatly meets the high-speed bandwidth requirements of data centers.
Category 7/Super Category 7 Network Cable: The outer side of the network cable is marked with CAT7 or CAT7A, with a maximum transmission frequency of 600/1000MHz and a transmission rate of 10Gbps. The core of Category 7 is generally made of copper wire with a thickness of about 0.57mm, which is high-purity oxygen free copper. This ensures ultra-low resistance, making the transmission longer and the signal more stable.
Category 8 Network Cable: Cat8 Category 8 Network Cable is the latest generation of double shielded (SFTP) network jumper, which has two wire pairs, can support a bandwidth of 2000MHz, and has a transmission rate of up to 40Gb/s. In addition, the Cat8 network cable can be compatible with all RJ45 cables and is designed specifically for 25/40GBASE-T applications. However, its transmission distance is short, only 30m, making it particularly suitable for connecting servers, switches, distribution frames, and other devices in short distance data centers.
According to whether to shield:
Network cables are further divided into shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP).
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
The outer layer is wrapped in a metal material, usually aluminum foil, to reduce radiation and prevent information from being eavesdropped. At the same time, it has a high data transmission rate, but the price is high, and the installation is also relatively complex.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
UTP has no metal shielding material, only one layer of insulation material wrapped around it, which is relatively cheap and flexible in networking. Except for some special occasions (such as areas with severe electromagnetic radiation), UTP is generally used. UTP is also the most commonly used network cable for household use.
The application environment of marine network cables is relatively complex, with a high level of electromagnetic interference. Generally, there are high requirements for shielding, which can be divided into the following types based on the overall screen and sub screen:
F/UTP: External aluminum foil overall screen, no shielding between wire pairs; CAT5E and CAT6 are commonly used.
SF/UTP: External copper wire weaving aluminum foil overall screen, no shielding between wire pairs, commonly used in CAT6.
S/FTP: External copper wire braid shielding, pair to pair aluminum foil shielding, good shielding effect, CAT6A and above will use this structure.
2.Differences in marine network cables
Compared to land network cables, marine network cables have significant differences in their installation and usage environment. For example, the electromagnetic environment on board is complex, the space is narrow, the air humidity and salinity are high, the outdoor ultraviolet radiation is strong, the oil pollution environment is high, the fire prevention requirements are high, the construction environment is harsh, and it is difficult to evacuate in case of accidents, which has higher requirements for the various performance of cables.
Marine network cables are generally designed according to the IEC 61156-5/6 standard. IEC 61156-5 is suitable for long-distance horizontal laying, mostly using solid core conductors, with good conductor integrity and longer and more stable signal transmission distance. IEC 61156-6 is suitable for working areas, such as computer room environments, where twisted conductors are commonly used, making cables more flexible and suitable for short distance narrow area laying. It is often used for jumpers.
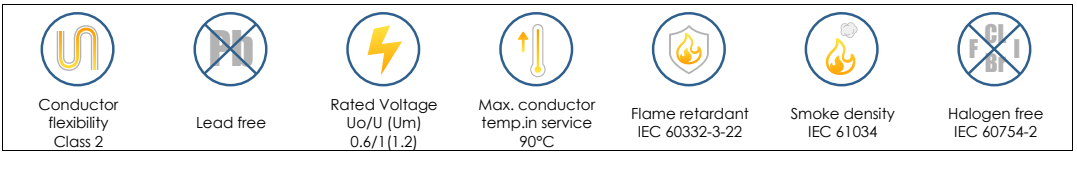
The general range of activities for ships is located on the sea surface. In the event of a fire, it is difficult for people to evacuate, and cables are flammable. The smoke generated by combustion can cause great harm to human health. In order to minimize the harm of fire accidents, marine network cables usually use low smoke and halogen-free (LSZH) flame retardant polyolefin as the outer sheath material, meeting the flame-retardant requirements of IEC60332 and the low smoke and halogen-free requirements of IEC 60754-1/2 and IEC 61034-1/2. In some special scenarios, fire-resistant cables with higher protection levels will be used, and fire-resistant materials such as mica tape will be added to meet the fire resistance requirements of IEC60331, ensuring that even after a fire, The circuit can also operate normally for a certain period of time, thereby maximizing the safety of people’s lives and property.
In some special marine environments, such as offshore oil refining platforms (FPSOs), large dredgers, etc., cables require long-term contact with sediment, oil slurry, and various corrosive substances. In order to effectively improve the strength of the cable outer sheath, cross-linked polyolefin (SHF2) or mud resistant (SHF2 MUD) outer sheath cables need to be used. Crosslinking polyolefins is a method of physical irradiation or chemical reaction crosslinking, which improves the performance of polyolefins and enables them to have a longer service life and better physical properties after crosslinking. Mud resistant cross-linked polyolefin refers to cross-linked polyolefin with stronger corrosion resistance and wear resistance, which enables cables to meet the mud resistance requirements of NEK 606 specification. In order to further improve the mechanical performance of the cable, metal armor will also be added to the cable, such as galvanized steel wire woven armor (GSWB), tinned copper wire woven armor (TCWB), etc. After adding metal armor, the cable will have better mechanical strength, thereby better protecting the network cable and reducing the occurrence of compression and tension fractures. At the same time, metal armor can also play a certain shielding role against external magnetic field interference, improving the integrity of data transmission.
In addition, marine network cables are generally required to be UV resistant (that is, UV resistant). Since ships and marine environments have sufficient sunshine, strong UV, and ordinary cables are easy to age, marine cables will use xenon lamps or water spray according to UL1581/ASTM G154-16 standards to reproduce the weathering effect of cables exposed to sunlight and rain during actual use, so as to test the anti-aging ability of cables.
Post time: Oct-26-2023